|
Task Management Software |
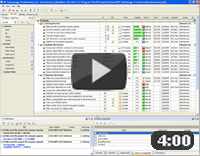 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
 TESTIMONIALS TESTIMONIALS
|
|
"...This is an excellent program. I'm so glad that I stumbled on to this when researching for task management programs. Very low learning curv, quite flexible, and the price is right. Tried at least 20 other programs, either too complicated, too expensive, or poor documentation..."
Chad Lindsey -
Honolulu, HI
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Problem Management Checklist |
|
|
|
|
|
|

 |
Problem management is a critical process of identifying and resolving any problems occurred in a project or within an organization. It plays an important role in revealing and solving issues. Use the following Problem Management Checklist to learn more on how to solve a problem.
|
| Order 750 checklists in MS Word and PDF printable format at $49.99 USD only. |
BUY NOW!  |
- Recognizing and Identifying a Problem.
- Unblock your ability to clearly think and recognize a problem. Frequently, fear and lack of self-confidence block our initiatives to solve a problem. Therefore, do not allow your emotions to intimidate your problem solving effort. Consider the following tips:
- Accept the fact that everything in your life or/and work cannot be foreseen.
- Admit that the strategy you select is your best solution at the given time.
- Admit that things around your problem may change and your solution may fail.
- Follow only workable procedures for finding solutions.
- Identify your problem. Once you’ve recognized that a problem exists, your next step is to identify it. You should enter the process rationally considering the fact that this process has an intellectual background and requires you to make some intellectual exercises to achieve success. Use your analytical skills to discover how the problem occurred. Ask yourself several questions to identify a problem:
- Did something go wrong?
- Was there a breakdown?
- Did you get some unexpected result or outcome?
- Can you say that there is something that is no longer workable?
- Define the nature of your problem. Use the following question list:
- Is your problem about people or machines in your organization?
- Is it with a particular employee or department, task or process, product or service, etc.?
- Is it something tangible or intangible?
- Is it an internal or external problem?
- Set the significance for your problem. When you set the level of significance (or priority) for your problem, you can better deal with it, considering its importance to you. Setting priorities allows you to make sure that your problem is rather small and it does not require much time and money. To set a priority, use the following question list:
- Does your problem cause disrupting operations?
- Does it hamper sales?
- Is it the major reason for causing conflicts among your employees?
- How frequent is your problem? (e.g. it occurs daily or once a week)
- Does it affect productivity of your personnel?
- Does it affect your goals?
- Does it affect relationships with your customers, vendors, or any other external people?
- Finding Solutions.
- There are four basic techniques, including Associations, Analogies, Brainstorming and Analytical Thinking. Let’s review each of the techniques.
- Associations. There is the technique of associative thinking that allows linking several objects together through either similarity or contiguity. This technique works as follows:
- Make a list of the problems you can think of.
- Within a short time limit, write as many ideas, which have either proximity or related cause to the listed problems, as you can generate.
- Now try to find relationships between the problems and ideas generated by your mind. Often the association technique allows finding unexpected relationships embedded in your problems.
- Analogies. This technique of analysis allows finding solutions through comparisons. You will need to compare different facets of your problem with other problems that may or may not have similar facets. By comparing your problem to analogous problems, you can define a more precise scope of your solution.
- Brainstorming. This problem solving method allows a group of people from diverse backgrounds to discuss various and different ideas for solutions by following group-discussion methods (brainstorming). To follow this technique, you should explain the problem to your group and encourage each group member to generate as many ideas for solutions as possible (no matter how ridiculous or farfetched these ideas may sound). Then all the ideas are to be discussed, revised and expanded by the group. The best ideas will be selected for a closer review.
- Analytical Thinking. This model of thinking is based on your skills and analytical abilities. It is one of the most conventional and logical methods of the process. It follows a pattern of logical steps, as shown below:
- Step #1. Investigate each reason for your problem. Then for each of the reasons you need to list potential solutions that may logically solve the problem.
- Step #2. Check your potential problem solutions with the research on how the problem might be solved by other people.
- Step #3. Use each of the listed thinking techniques (Associations, Analogies, Brainstorming) to search for possible solutions. You should design a list of solutions and investigate every possible solution (even if there will be solutions that seem to be unrealizable, too simple, or even stupid). The effect of this step is to give you a rich set of ideas that will lead you to the best solution.
- Choose the best solution. By following one of the listed techniques you will find a set of possible solutions for your problem. Now it is time to sort out and select the most appropriate solution. To do so, you should check each solution against the following criteria: Cost effectiveness, Time constraints, Availability of resources (manpower, material, etc.), and Your own intuition. The following questions will help you define the best solution:
- Are the goals of one or another solution sound and clear to you?
- Will the solution help you achieve your own objectives?
- Will the solution help you carry out your responsibilities ?
- Can you set metrics for the solution?
- Taking Actions.
- Design a plan of actions. Once the best solution is identified, you need to develop an action plan and follow it to implement the solution and achieve your goals . Note that even the best solution can fail if it is not carried out correctly. When designing your document of actions, consider the following question list:
- Who will be involved in the solution implementation?
- Who will be affected by the solution?
- How should your action plan be presented to your employees, customers, vendors, etc.?
- How often is it required to take actions for implementing solutions?
- What are the deadlines for the solution implementation?
- Where will you implement the solution?
- How will it happen?
- What is required to make it happen?
- Design a diagram for your actions. Such a diagram will give you a graph representation of your action plan allowing you to track each of the actions and measure your success. To build your diagram, you can use software that can be easily found In Internet.
- Analyze your actions. Analyzing how you follow your plan of actions allows you to see if you've considered as many of the activities as possible. Use the following question list to analyze your actions:
- Have you involved adequate staff that can help you carry out your action plan?
- Have you designed a detailed yet simple plan that can be easily comprehended and followed by your employees involved in the process?
- Have you organized a meeting to present the plan and discuss its items before the implementation phase?
- Have you set realistic and feasible deadlines for your plan of actions?
- Have you assigned roles and responsibilities to your employees involved in the action plan implementation?
- Can you say your action plan is cost-effective?
- Have you shared the plan and made it available to all people involved in the implementation process?
| Order 750 checklists in MS Word and PDF printable format at $49.99 USD only. |
BUY NOW!  |
|





 |
CentriQS Tasks Management Solution 
Looking for multi-user task management software? Try CentriQS complete task management solution for planning, tracking and reporting tasks, projects, and schedules. Increase productivity of your small business or office by better organizing your employees' tasks and time.
 FREE Download CentriQS FREE Download CentriQS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CentriQS  -15% OFF -15% OFF |
All-in-one business management software
for small and midsize enterprises |
 |
|
|
| VIP Task Manager |
Multi-user project management software
to plan, schedule and track project tasks. |
 |
|
|
| VIP Checklists
|
More than 750 ready-to-use to-do lists
to plan your personal and business life |
 |
|
|
| VIP Team To Do List |
Professional task management software
to make and send team todo lists by email |
 |
|
|
| VIP Organizer |
Personal time management software
to organize time at home and at work |
 |
|
|
| VIP Simple To Do List
|
Simple and effective to-do list software
to plan daily chores, trips, wedding, etc. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|